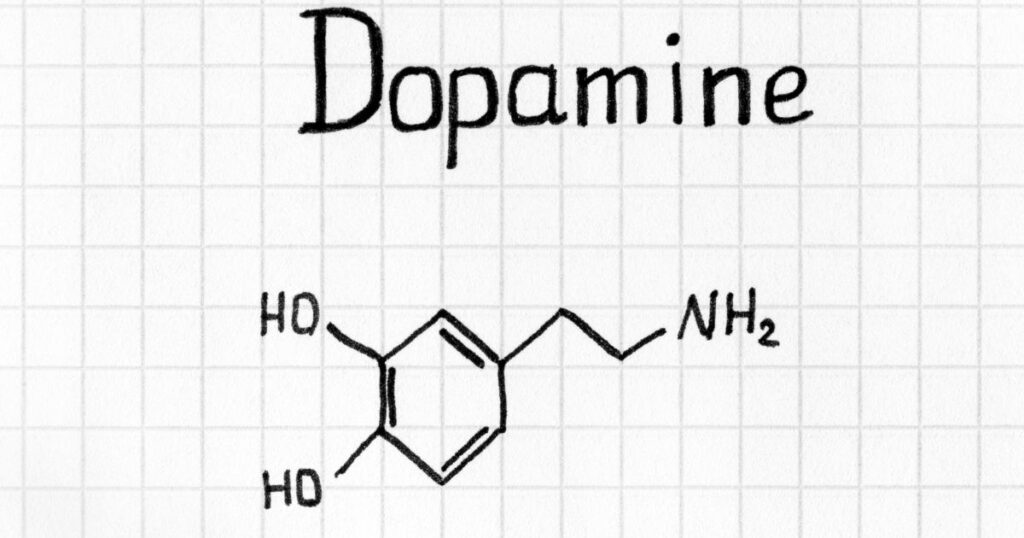
In the world of neuroscientific research, understanding how dopamine receptors interact is important. These interactions are important for comprehending behaviors and mechanisms related to reward, addiction, and mental health disorders. This is where 2 MMC, a substance that aids in these investigations, comes into play. 2 MMC helps scientists explore the complex relationships between dopamine receptors, offering insights into how these receptors influence brain function and behavior.
Exploring ways to purchase 2 MMC online(2 MMC en Línea) can be significant for researchers seeking to conduct detailed studies on these interactions. Researchers can unlock potential therapeutic targets for various neurological and psychiatric conditions by investigating the dynamics of dopamine receptors. This could lead to innovative treatments that could improve the quality of life for many individuals.
The ability to examine dopamine receptor interactions closely allows researchers to make connections that may go unnoticed otherwise. 2 MMC can be a necessary tool in these studies since it helps reveal the roles different receptors play in brain activity. Whether you’re a scientist or someone intrigued by the workings of the brain, learning about these interactions can be fascinating and insightful. Additionally, finding reliable options for this compound, such as a specific supplier, guarantees that research can continue unabated, leading to groundbreaking discoveries.
Understanding Dopamine Receptor Mechanisms
Dopamine receptors play a significant role in various brain functions, including mood, motivation, and reward. These receptors can be categorized into distinct groups based on their functions and how they interact with their environment.
Classification and Function of Dopamine Receptors
Dopamine receptors are divided into two main families: D1-like and D2-like receptors. D1-like receptors include D1 and D5 subtypes. They typically activate pathways that result in the production of cyclic AMP (cAMP). This influences many physiological responses.
On the other hand, D2-like receptors consist of D2, D3, and D4 subtypes. These often inhibit cAMP production, impacting different neuronal circuits. Understanding this classification helps in guiding research into neurological disorders where dopamine dysfunction is common.
2-MMC’s Influence on Dopamine Signaling Pathways
2-MMC, a research chemical, is used to study how dopamine interacts with its receptors. In particular, 2-MMC affects dopamine signaling pathways by influencing how these receptors respond to neurotransmitters.
By altering binding dynamics, 2-MMC helps researchers observe changes in the cAMP production and the broader impacts within the signaling pathways. Success in this way of influencing receptor activity gives important insights into conditions like schizophrenia.
Receptor Activation and Ligand Binding Dynamics
Ligand binding is fundamental in how dopamine receptors function. This process dictates a receptor’s activation or inhibition. For example, when a ligand binds to a D2-like receptor, it prevents the activation of adenylyl cyclase, which reduces cAMP levels.
G Protein coupling plays a necessary role here, with different binding modes impacting receptor response. This regulates how signals are sent through neurons, affecting behaviors and responses to drugs.
Emerging Insights from Cryo-Electron Microscopy Studies
Recent advances in cryo-electron microscopy allow scientists to visualize the structural organization of dopamine receptors in great detail. This technique improves understanding of the structural basis for ligand binding.
Cryo-EM studies reveal complex interactions and hydrophobic interactions within the receptor structure, which are key to their function. These insights are important for developing therapeutic strategies aimed at correcting receptor malfunctions.
Therapeutic Implications and Psychiatric Research
2-MMC shows promise in addressing neuropsychiatric disorders. Understanding its role can lead to new drug targets and potentially beneficial therapeutic effects.
The Role of 2-MMC in Neuropsychiatric Disorders
You might find 2-MMC significant in researching conditions like schizophrenia and depression. It can help you understand how the dopaminergic system functions in these disorders. Researchers study 2-MMC to explore alterations in dopamine receptor activity, which is linked to symptoms of neuropsychiatric diseases.
Neuroinflammation and neurodevelopment also play a part in these conditions. By examining these interactions, insights into the progression of diseases such as Parkinson’s could unfold. This offers a gateway to discovering therapeutic effects and improving treatment approaches.
Drug Development and Therapeutic Targets
In drug development, 2-MMC offers potential as a therapeutic target for neurological and psychiatric diseases. You see it applied in testing new medications aimed at modifying dopamine receptor function. This includes targeting specific receptor subtypes for improved drug efficacy.
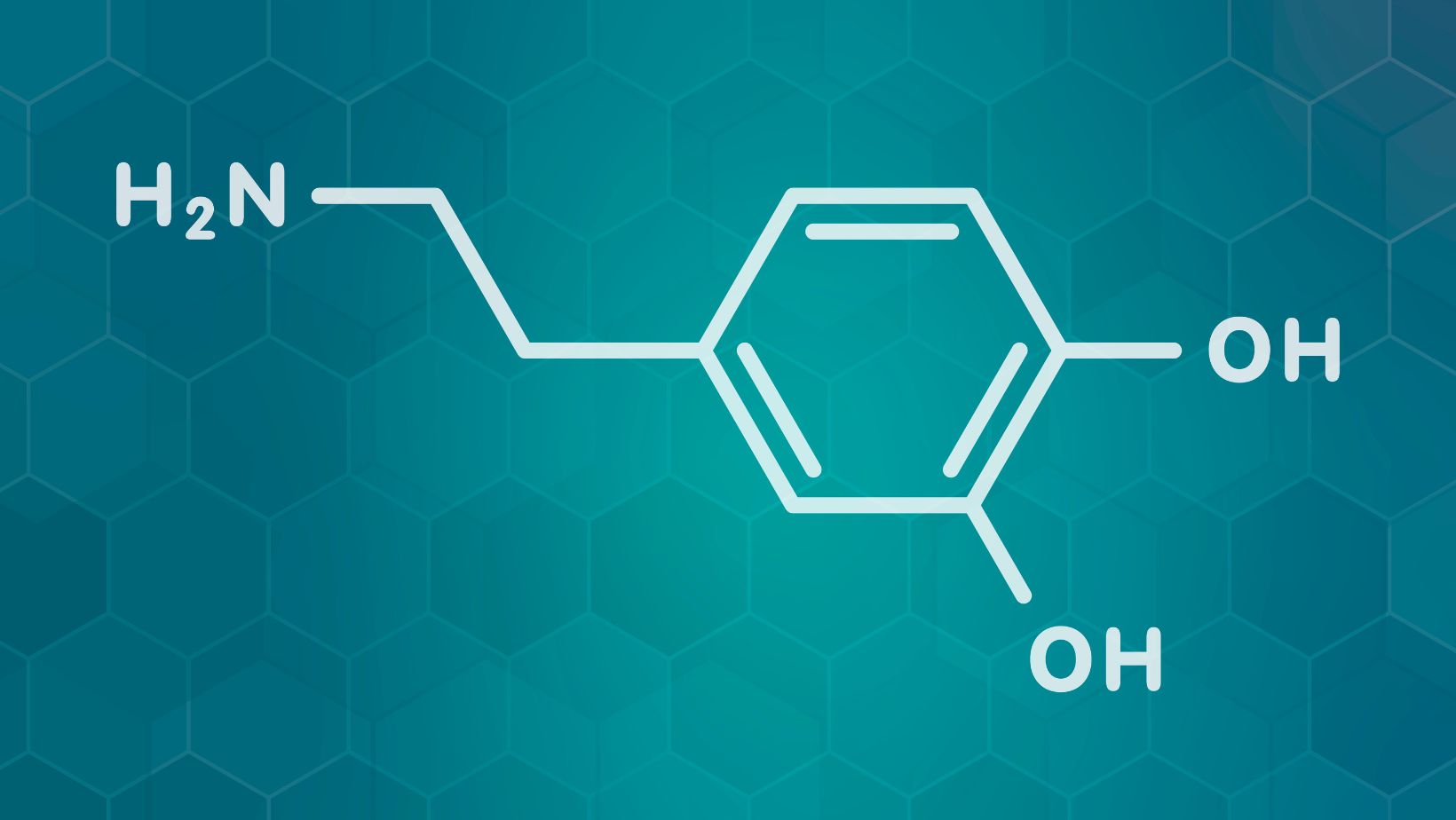
2-MMC’s involvement in brain function provides insights into treating disorders like depression. It could influence the action of drugs that affect the dopaminergic system. By advancing knowledge of receptor interactions, 2-MMC aids in identifying less invasive treatment methods and broadens therapeutic options for patients.
Potential for Addiction and Side Effects
When considering the use of 2-MMC, you need to be aware of its potential for addiction and side effects. Just like other psychoactive substances, it may contribute to drug abuse. Monitoring its impact on brain function helps assess these risks.
The possibility of unwanted side effects connected to dopamine receptor interactions cannot be ignored. Effects on neuropsychiatric disorders need careful evaluation to avoid worsening conditions. This is especially true in the treatment of diseases such as Parkinson’s and schizophrenia, where the balance between therapeutic benefits and potential harm must be managed.
By paying attention to these factors, more informed decisions about its use in therapy can be made. This can direct future research and application strategies.
Conclusion
You have explored how 2 MMC contributes to understanding dopamine receptor interactions. This research advances neuroscientific studies by helping to analyze receptor mechanisms.
2 MMC is often used as a tool in experiments due to its specific impact on receptors. It helps researchers identify binding sites and their effects on signal pathways.
By using 2 MMC, you gain a better grasp of dopamine’s role in brain functions, such as motivation and memory. This matters because these insights can lead to new treatments for disorders linked to dopamine dysregulation.